HashiCorp Terraform is an infrastructure as code tool that lets you define both cloud and on-prem resources in human-readable configuration files that you can version, reuse, and share. You can then use a consistent workflow to provision and manage all of your infrastructure throughout its lifecycle. Terraform can manage low-level components like compute, storage, and networking resources, as well as high-level components like DNS entries and SaaS features.
Hands On: Try the Get Started tutorials to start managing infrastructure on popular cloud providers: Amazon Web Services, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, and Docker.
Terraform creates and manages resources on cloud platforms and other services through their application programming interfaces (APIs). Providers enable Terraform to work with virtually any platform or service with an accessible API.
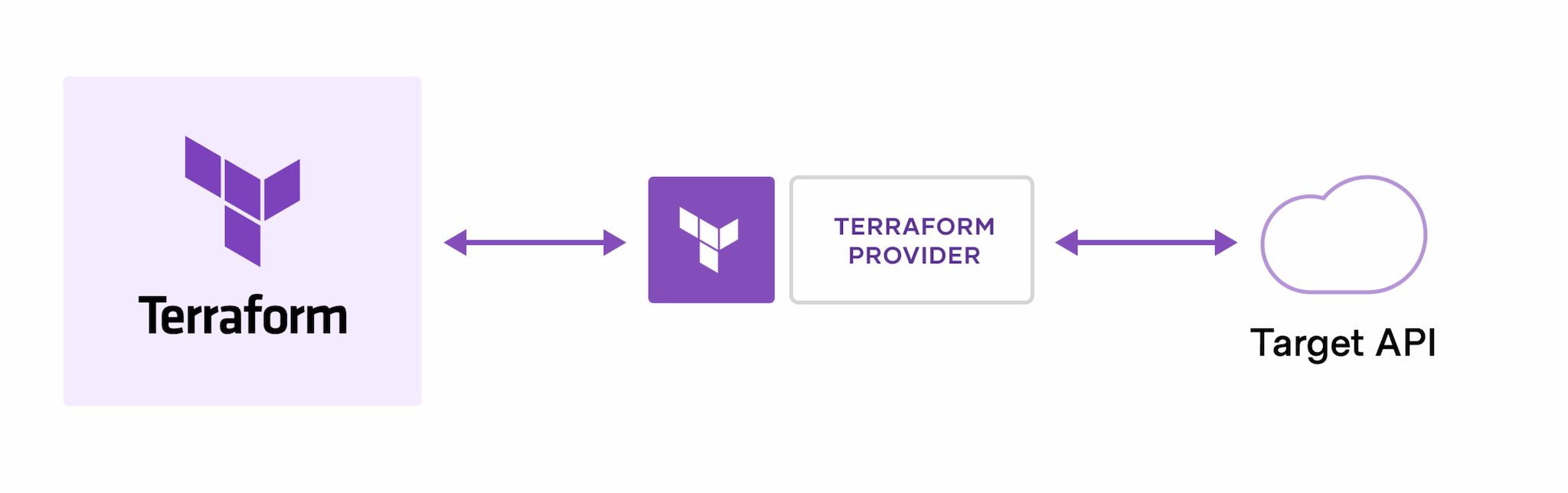
HashiCorp and the Terraform community have already written more than 1700 providers to manage thousands of different types of resources and services, and this number continues to grow. You can find all publicly available providers on the Terraform Registry, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Kubernetes, Helm, GitHub, Splunk, DataDog, and many more.
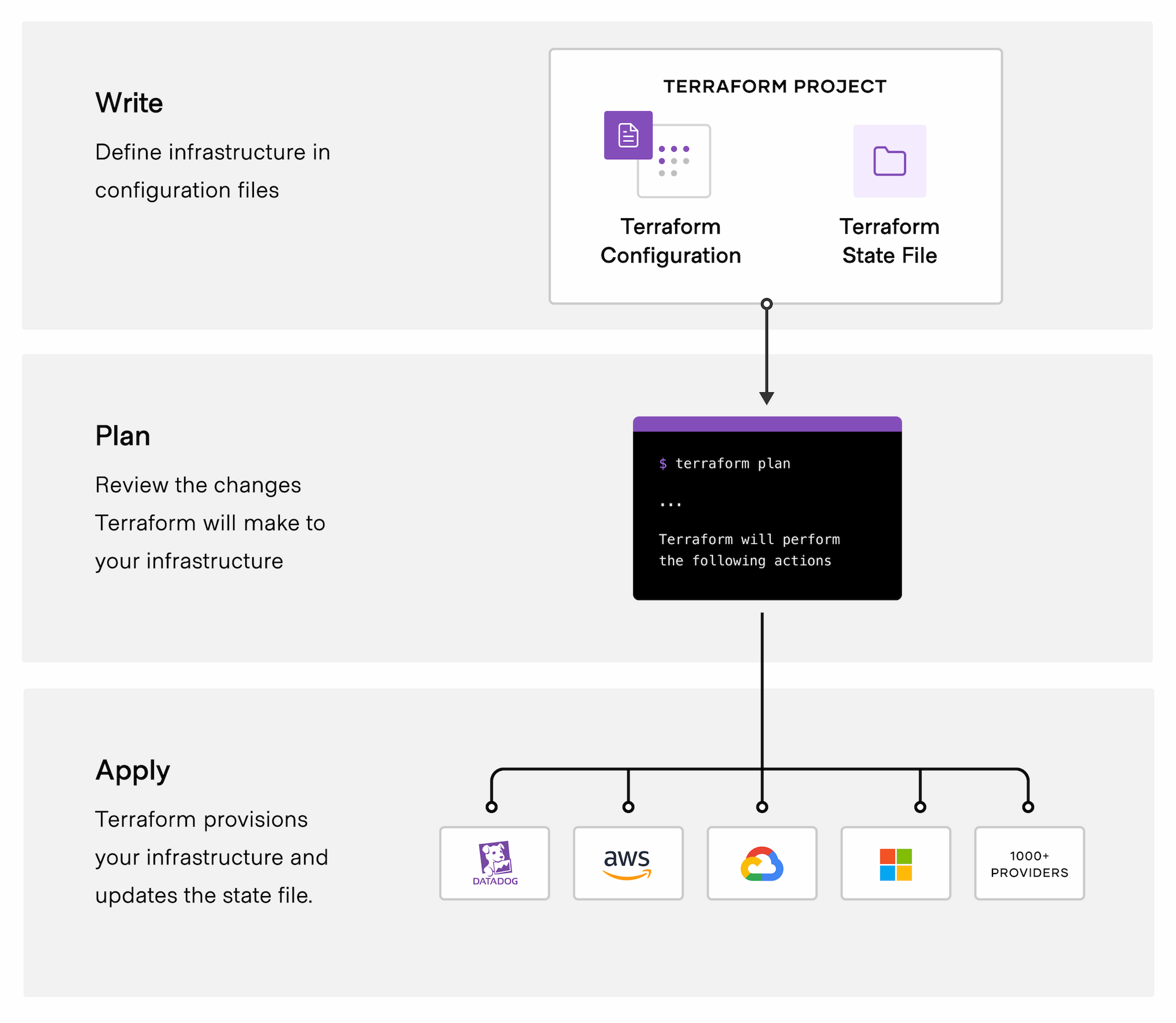
The core Terraform workflow consists of three stages: